Juice, nature’s liquid treasure, has long captivated our taste buds with its vibrant colors, refreshing flavors, and undeniable health appeal. From tangy orange nectar to the lush green elixirs of nature’s garden, juice has a remarkable ability to invigorate our senses and quench our thirst. But have you ever wondered what lies beyond its delightful taste? What does juice do to your body?

In this article, we embark on a captivating journey into the depths of the human body, exploring the transformative effects that juice can have on our overall well-being. Beyond its undeniable hydrating properties, juice possesses a secret arsenal of nutrients, antioxidants, and enzymes that can bestow numerous benefits upon us. So, let us delve into the science behind the sip, uncovering the remarkable ways in which juice can nurture and revitalize our bodies.
As we uncover the secrets hidden within these tantalizing elixirs, we will explore how juice fuels our bodies with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, bolstering our immune system and fortifying our defenses against illness. We’ll shed light on the digestive wonders of fiber-rich juices, promoting gut health and facilitating smooth digestion. Moreover, we will examine how juice’s natural sugars provide a quick source of energy, while offering valuable insights into weight management and overall vitality.
However, it’s not all sunshine and sweetness. We must also tread cautiously, discerning the potential pitfalls of excessive sugar intake, understanding the nuances between store-bought and homemade juices, and emphasizing the importance of moderation in our juice consumption.
So, whether you are a juice enthusiast seeking to deepen your understanding or a curious newcomer eager to unlock the secrets of this flavorful elixir, join us on this illuminating exploration. Together, we will unravel the remarkable effects of juice on the human body, empowering you with knowledge to make informed choices about this liquid ally in your quest for a healthier, more vibrant life.
What Does Juice Do To Your Body
Juice, particularly fruit and vegetable juice, can have several effects on the body due to its nutritional content.
Here are some of the ways juice can impact your body:
- Hydration: Juices are primarily composed of water, which helps maintain proper hydration levels in the body. Staying hydrated is essential for various bodily functions, including digestion, circulation, and temperature regulation.
- Nutrient intake: Depending on the type of juice, it can provide a range of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. For instance, orange juice is rich in vitamin C, while carrot juice is high in beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A. Consuming juices can help supplement your nutrient intake, especially if you struggle to consume enough fruits and vegetables through solid food alone.
- Antioxidant boost: Many fruits and vegetables used in juices are abundant in antioxidants. These compounds help protect the body against oxidative stress caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. Antioxidants neutralize free radicals, which can lower the risk of chronic diseases and support overall health.
- Digestive health: Some juices, particularly those made from fibrous fruits and vegetables, can aid digestion. The fiber content in these juices adds bulk to the stool, promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Additionally, certain fruits like pineapple and papaya contain enzymes (bromelain and papain, respectively) that can aid in digestion.
- Boosting immune system: Juices high in vitamin C, such as orange juice, can support immune function. Vitamin C is known for its role in strengthening the immune system and helping the body fight off infections. Including vitamin C-rich juices in your diet can contribute to a healthy immune response.
- Energy and vitality: Juices can provide a quick source of energy due to their natural sugars, such as fructose. However, it’s important to note that the sugar content in juices can be concentrated compared to whole fruits, which may lead to a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. It’s generally recommended to consume juices in moderation and choose those with lower sugar content or opt for whole fruits when possible.
- Weight management: Juices can be a part of a balanced diet when consumed in moderation. As they are often lower in calories compared to sugary beverages like sodas or energy drinks, incorporating healthier juice options can be beneficial for weight management. However, it’s crucial to be mindful of portion sizes and avoid excessive consumption of high-calorie or sweetened juices.
It’s worth mentioning that not all juices are created equal. Some store-bought juices may contain added sugars, preservatives, or lack the fiber found in whole fruits and vegetables. Therefore, it’s generally recommended to make your own juices or choose fresh, cold-pressed juices with minimal additives to maximize the nutritional benefits.
Lastly, it’s important to note that while juice can provide certain benefits, it should not replace whole fruits and vegetables in your diet. Whole foods offer additional benefits like fiber and chewing, which can contribute to satiety and overall digestive health. Juices can be a healthy addition to a well-rounded diet but should be consumed as part of a balanced approach to nutrition.
Where Does Juice Go When You Drink It
When you drink juice, it goes through a process called digestion, where it travels through your digestive system and is eventually absorbed into your body. Here’s a breakdown of what happens to juice after you drink it:
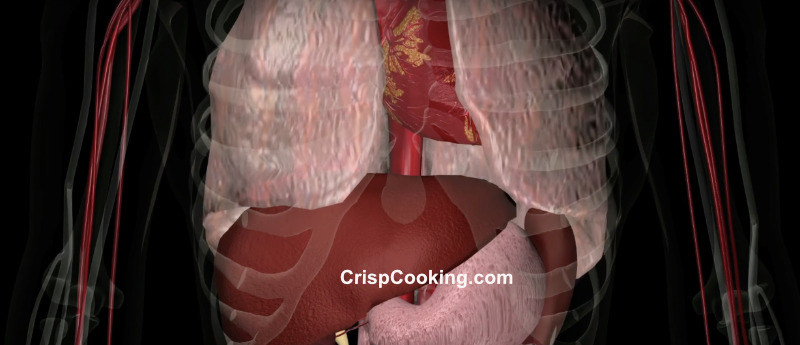
- Mouth: As you sip and swallow the juice, it enters your mouth, where it mixes with saliva. Saliva contains enzymes that begin breaking down carbohydrates present in the juice.
- Esophagus: The juice travels down the esophagus, a muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. The muscles in the esophagus contract in a wave-like motion, called peristalsis, to push the juice toward the stomach.
- Stomach: In the stomach, the juice mixes with stomach acid and digestive enzymes. The acid helps break down the juice further, while the enzymes begin to break down the proteins and other nutrients present in the juice. The stomach’s muscular contractions continue to mix the juice, turning it into a semi-liquid substance called chyme.
- Small Intestine: The chyme then enters the small intestine, where most of the absorption of nutrients takes place. The walls of the small intestine contain tiny finger-like projections called villi, which increase the surface area for nutrient absorption. The nutrients from the juice, including sugars, vitamins, minerals, and other compounds, are absorbed into the bloodstream through the villi.
- Liver and Pancreas: As the absorbed nutrients enter the bloodstream, they are transported to the liver. The liver helps regulate nutrient levels in the blood and performs various metabolic functions. The pancreas also plays a role by releasing digestive enzymes to further break down nutrients.
- Large Intestine: Any undigested fiber and some remaining water from the juice pass into the large intestine, also known as the colon. In the colon, water is reabsorbed, and the remaining fiber helps promote regular bowel movements and provides nourishment to beneficial gut bacteria.
- Rectum and Elimination: The waste material, including indigestible fiber and other undigested components from the juice, moves into the rectum. The rectum stores the waste until it is ready to be eliminated from the body as stool during a bowel movement.
It’s important to note that the exact journey of juice through the digestive system can vary based on factors like the composition of the juice, individual metabolism, and overall health. Additionally, different components of the juice, such as water and nutrients, may be absorbed at different points along the digestive tract.
Overall, the process of digestion allows the body to extract the nutrients from the juice and utilize them for various bodily functions, while waste materials are eliminated.
Difference Between Juice and Nectar
Juice and nectar are both liquid beverages made from fruits, but there are differences in their composition and processing methods.

Here’s a breakdown of the main differences between juice and nectar:
- Fruit Content: Juice is typically made by extracting the liquid from fruits, while nectar is made by blending fruit puree or juice with water and sweeteners.
- Fruit Pulp: Juice is usually strained to remove the fruit pulp, resulting in a clear liquid. Nectar, on the other hand, retains some of the fruit pulp, giving it a thicker and more textured consistency.
- Sweeteners: Juice is typically made solely from the natural sugars present in the fruit, without any added sweeteners. Nectar, on the other hand, may contain added sweeteners, such as sugar, corn syrup, or artificial sweeteners, to enhance the taste and sweetness.
- Fruit Concentration: Juice is often consumed as a ready-to-drink beverage and is typically made from 100% fruit juice, though there are variations with varying percentages of fruit content. Nectar, on the other hand, is often diluted with water and may contain a lower percentage of fruit content. The specific fruit content required for a beverage to be classified as nectar can vary by country or region.
- Labeling: In many countries, the labeling regulations distinguish between juice and nectar based on the fruit content. For a beverage to be labeled as “juice,” it typically needs to meet certain criteria, such as being made solely from fruit juice without added sweeteners or dilution. Nectar, on the other hand, may have specific requirements for minimum fruit content or the addition of sweeteners.
It’s important to note that the terminology and regulations regarding juice and nectar can vary across different countries and regions. It’s advisable to read the product labels or familiarize yourself with the local regulations to understand the specific composition and fruit content of the juice or nectar you are consuming.
When choosing between juice and nectar, consider your preferences and dietary needs. Juice, with its clearer consistency and higher fruit content, may be a preferred choice for those seeking a more direct fruit flavor without added sweeteners. Nectar, with its thicker texture and sometimes lower fruit content, can offer a more indulgent taste experience. Remember to check the ingredient list and nutritional information to make informed choices based on your preferences and health goals.
FAQs About Juicing
Can I juice zucchini?
Yes, zucchini can be juiced. While zucchini is not typically the first vegetable that comes to mind for juicing, it can be a healthy and versatile addition to your juice recipes. Zucchini is low in calories, high in water content, and packed with essential nutrients such as vitamin C, vitamin A, potassium, and dietary fiber.
To juice zucchini, you will need a juicer capable of handling vegetables. Here’s a simple method to juice zucchini:
1. Wash the zucchini thoroughly to remove any dirt or debris.
2. Trim off the ends of the zucchini.
3. Cut the zucchini into smaller pieces that will fit through the juicer chute.
4. Feed the zucchini pieces into the juicer, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
5. Collect the fresh zucchini juice in a container or glass.
6. Optionally, you can strain the juice through a fine-mesh sieve to remove any remaining pulp or fiber.
Zucchini juice can be consumed on its own or combined with other fruits and vegetables to create a custom juice blend. Its mild flavor makes it a versatile ingredient that can be easily paired with various fruits like apples, cucumbers, lemons, or ginger to enhance the taste and nutritional profile of your juice.
Keep in mind that zucchini juice is best consumed fresh to retain its nutritional value and taste. If stored, it may separate, so be sure to give it a good stir or shake before drinking.
Experiment with different combinations and proportions to find a zucchini juice recipe that suits your taste preferences and nutritional needs. Enjoy the goodness of zucchini in liquid form and reap the benefits it offers for your body.
Is V8 Juice Keto?

V8 juice, in its original form, is not considered to be strictly keto-friendly due to its relatively higher carbohydrate content. While V8 juice contains a blend of vegetables and can provide some essential nutrients, it also contains a significant amount of natural sugars from the vegetables it includes.
The carbohydrate content of V8 juice can vary depending on the specific variety and serving size. On average, an 8-ounce (240 ml) serving of original V8 juice contains around 10-11 grams of carbohydrates, with some of those grams coming from fiber.
For individuals following a strict ketogenic diet, which typically requires limiting carbohydrate intake to very low levels (often around 20-50 grams per day), V8 juice may not fit within their daily carbohydrate allowance.
However, it’s worth mentioning that V8 offers a range of juice options, including low-sodium versions and blends with added fruits. Some of these variations may have reduced carbohydrate content, but it’s essential to carefully read the nutrition labels and check the specific carbohydrate content to determine if they align with your keto goals.
If you are following a ketogenic diet, it is generally recommended to prioritize whole, unprocessed foods that are naturally low in carbohydrates, such as leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, avocados, and healthy fats like olive oil and coconut oil. These options are typically more suitable for a keto diet and can provide the necessary nutrients without compromising your desired macronutrient ratios.
Always consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet, especially if you have specific dietary requirements or health concerns. They can provide personalized advice and guidance based on your unique needs.
Does cranberry juice have d-mannose?
Yes, cranberry juice contains a naturally occurring sugar called D-mannose. D-mannose is a type of simple sugar that is present in small amounts in various fruits, including cranberries.
D-mannose is often associated with its potential benefits for urinary tract health. It is believed to help prevent certain types of bacteria, particularly Escherichia coli (E. coli), from adhering to the walls of the urinary tract, which can reduce the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs).
While cranberry juice does contain D-mannose, it’s important to note that the concentration of D-mannose in cranberry juice may not be as high as in certain D-mannose supplements specifically formulated for UTI prevention. If you are considering using D-mannose for urinary tract health, it may be more effective to use a D-mannose supplement with a higher concentration of the sugar.
Additionally, it’s worth noting that many commercial cranberry juices often contain added sugars or are blended with other fruits, which can increase the overall carbohydrate content and potentially counteract some of the potential benefits. When choosing cranberry juice, look for options with no added sugars or consider using pure cranberry juice or concentrated cranberry supplements to maximize the D-mannose content while minimizing unnecessary additives.
What fruit juice is good for arthritis?
While there is no specific fruit juice that can cure or treat arthritis, certain fruits and their juices may offer potential benefits for individuals with arthritis due to their anti-inflammatory properties and nutritional content. Here are some fruit juices that may be beneficial for arthritis:
1. Tart cherry juice: Tart cherries contain compounds called anthocyanins, which have been associated with anti-inflammatory effects. Some studies have suggested that tart cherry juice may help reduce joint pain and inflammation in individuals with arthritis.
2. Pineapple juice: Pineapples contain an enzyme called bromelain, which has anti-inflammatory properties. Bromelain may help reduce pain and inflammation associated with arthritis. Pineapple juice can be a refreshing option to include in your diet, but it’s worth noting that the concentration of bromelain in juice may be lower compared to consuming fresh pineapple.
3. Orange juice: Oranges are rich in vitamin C, which is known for its antioxidant properties. Vitamin C helps protect the body against oxidative stress, which can contribute to inflammation. Orange juice can provide a vitamin C boost, which may support overall joint health.
4. Pomegranate juice: Pomegranates are a rich source of antioxidants, including anthocyanins and polyphenols. These compounds have shown potential anti-inflammatory effects and may help reduce joint pain and inflammation associated with arthritis.
5. Grape juice: Grapes contain resveratrol, a compound with anti-inflammatory properties. Resveratrol may help reduce inflammation and provide joint health benefits. Opt for 100% pure grape juice without added sugars for the best nutritional value.
It’s important to note that while these fruit juices may have potential benefits for arthritis, they should be consumed as part of a balanced diet and should not replace any prescribed medications or treatments for arthritis.
Additionally, individual responses to these juices may vary, so it’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized dietary recommendations based on your specific needs and condition.
Final Thoughts
As we reach the end of our exploration into the effects of juice on the human body, we are left with a deeper understanding of the transformative power held within those colorful elixirs. Juice, in its various forms, has shown us that it is not just a refreshing beverage but a potent source of essential nutrients, antioxidants, and hydration.
From its ability to fortify our immune system and support overall well-being to its role in promoting digestion and providing a quick burst of energy, juice has a remarkable impact on our bodies. The diverse array of fruits and vegetables used to create juice offers a wide range of health benefits, allowing us to customize our intake based on our unique needs and taste preferences.
However, it’s crucial to approach juice consumption with balance and moderation. While juice can provide valuable nutrients, it is important to be mindful of added sugars, potential dilution with water, and the impact on blood sugar levels. Opting for homemade or freshly squeezed juices can help ensure maximum nutritional value and minimize unnecessary additives.
Moreover, it’s worth recognizing that juice is not a substitute for a well-rounded diet that includes a variety of whole fruits, vegetables, and other nutritious foods. Whole foods offer the added benefits of fiber, which promotes satiety, digestive health, and a diverse gut microbiome.
In the grand tapestry of a healthy lifestyle, juice can be a vibrant thread, contributing to our overall wellness. By incorporating a balanced approach to juice consumption, we can harness its potential benefits and savor the delightful flavors that nature provides.
So, let us raise a glass to the wonders of juice, celebrating its ability to nourish, rejuvenate, and delight our bodies. As we continue on our journey towards optimal health, let us make informed choices, embracing the goodness that juice offers while keeping a holistic perspective on our well-being.
Cheers to the transformative power of juice and to a life filled with vitality and abundance.
Hello, I am Cristy. I love cooking but what I love most is keeping my kitchen tools and appliances top notch. I enjoy writing about everything I have learned around the kitchen. I believe that keeping your kitchen tools well cleaned and maintained produces the best dishes and drinks. Besides writing and cooking I enjoy traveling, camping, hiking and music.
